- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
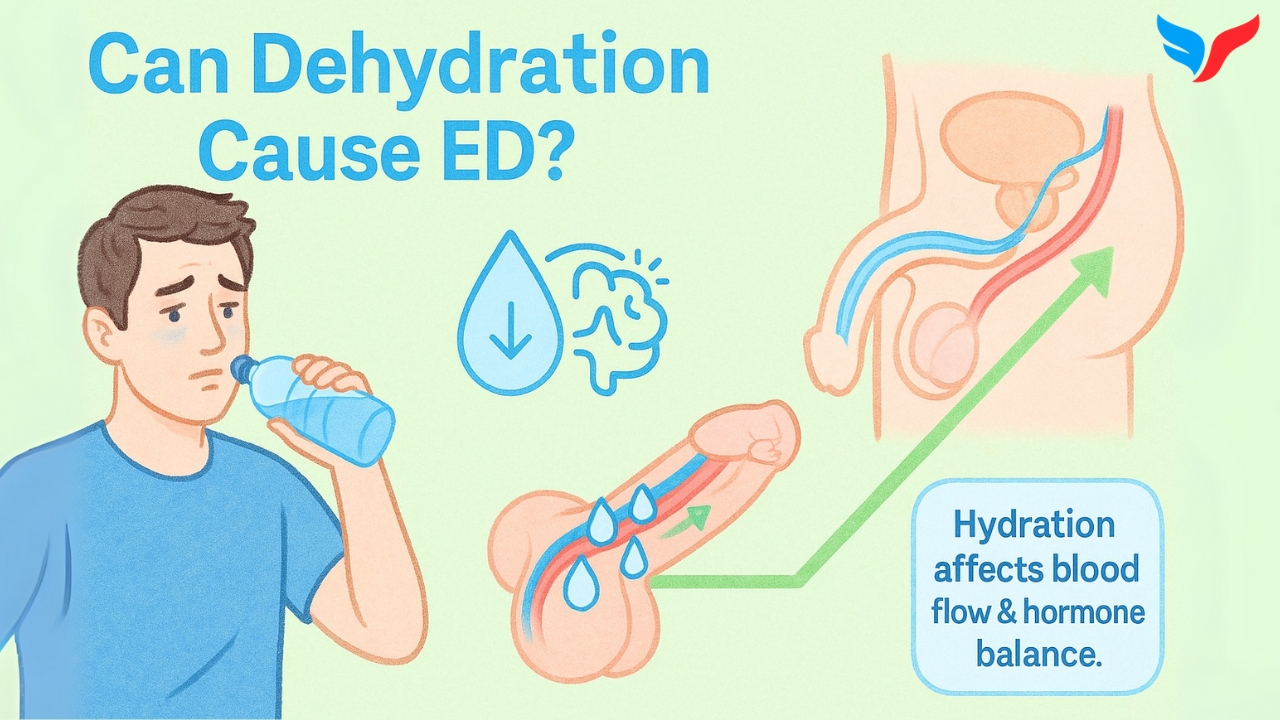
Can Dehydration Cause ED?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common condition that affects many men. It means having trouble getting or keeping an erection. Studies show that up to 76.5% of men might have some form of ED during their lives. In the U.S., more than 3 out of 10 men between the ages of 40 and 70 deal with this issue. Doctors usually look at medical problems like heart disease, diabetes, nerve issues, or mental health problems as the main causes. But sometimes, lifestyle habits that can be changed also play a big role and often get missed.
As a urologist at FableWings, I often talk about everyday habits that may quietly affect men’s sexual health, one of them being staying hydrated. While most medical guides don’t list dehydration as a leading cause of ED, emerging research suggests that not drinking enough water might actually impact a man’s ability to achieve or maintain an erection. This matters because ED can sometimes be an early sign that something deeper in the body vascular, hormonal, or neurological, isn’t functioning properly. That’s why it’s important to consider all possible triggers, even simple ones like water intake. Similarly, questions like “Does Adderall cause ED?” or “Does Lisinopril cause ED?” are becoming more common among patients, reminding us that both lifestyle habits and medications can play a role in sexual health. Understanding these subtle connections helps us take a more holistic and proactive approach to managing erectile dysfunction.
We’ll explain how being dehydrated might lead to ED, how to tell if dehydration is a factor, and what can happen if someone doesn’t drink enough water over time. We’ll also give tips for doctors on how to help patients with this issue. The goal is to help healthcare providers better understand how something as basic as water can impact men’s health and give people the knowledge they need to take care of themselves.
How Dehydration Affects Erections?
Not drinking enough water can make it harder for the body to get or keep an erection. Here are two big ways dehydration causes problems:

Less Blood Flow
When you’re dehydrated, your body has less blood to move around. Erections depend on having enough blood flow to the penis. If there isn’t enough blood, the penis can’t fill up properly, making erections weak or hard to get. Also, when water is low, the body tightens blood vessels to keep your blood pressure stable and protect important organs. But this also means less blood goes to areas like the penis, making erections even harder to achieve.
Tighten Blood Vessels
When you’re low on water, your body releases hormones that make blood vessels tighter. Two important ones are called angiotensin II and vasopressin. These hormones help save water and keep blood pressure up. But they also make blood vessels smaller, including the ones in the penis. Studies have shown that high levels of these hormones can make it harder for blood to flow where it needs to go for an erection. One study even showed that vasopressin made the muscles in the penis squeeze too much, which can stop an erection from happening.

Blood Pressure Changes
When you don’t drink enough water, your body has less fluid to pump around. This can lead to low blood pressure, especially when standing up. A certain amount of pressure is needed to send blood to the penis for an erection. If blood pressure is too low, it’s harder to get or keep an erection. But here’s the tricky part: your body tries to fix low pressure by tightening blood vessels. It does this using special chemicals like angiotensin II and vasopressin. These can raise your blood pressure too much. So, dehydration might make your pressure go too low at first, then too high later. Both situations are bad for erections. Low pressure means not enough blood gets to the penis, and high pressure over time can damage the blood vessels. To have healthy erections, you need steady blood pressure and flexible blood vessels, something dehydration messes with.

Hormonal Changes
Water is very important for keeping your hormones balanced. If you don’t drink enough water for a long time, it can mess with the hormones that help with sexual health. Testosterone is the main male sex hormone. It helps with sex drive, erections, and the chemical (called nitric oxide) that helps blood flow to the penis. Some studies have shown that men who are dehydrated have lower testosterone levels. For example, one study on athletes showed that when they lost water quickly, their testosterone went down, and a stress hormone called cortisol went up. The more dehydrated they were, the worse their hormone levels got. This happens because your body sees dehydration as a stress and starts to release stress hormones. These can block normal testosterone production. Low testosterone can lead to a lower sex drive and weaker erections. On top of that, stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline can activate the body’s “fight or flight” mode, which is the opposite of the calm, relaxed state needed for an erection. So, when your hormones are out of balance from dehydration, it can make sexual performance harder.
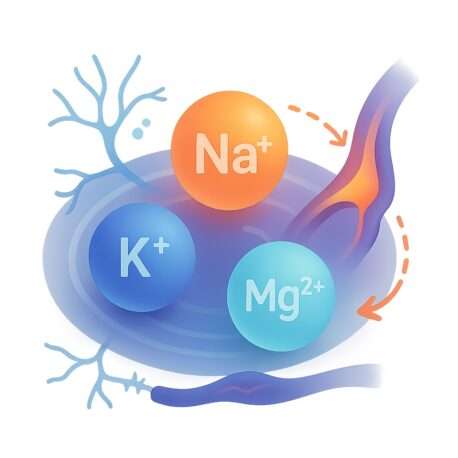
Mineral Imbalances
Your body also needs the right balance of minerals, called electrolytes, like sodium, potassium, and magnesium. These help your muscles and nerves work correctly. When you’re dehydrated, these minerals can get too high or too low, which causes problems. Too much sodium, for example, makes your body release vasopressin, a hormone that tightens your blood vessels. Not having enough potassium or magnesium can also cause blood vessels to tighten or nerves to work improperly. When your blood vessels are tight and nerves aren’t sending the right signals, it’s even harder for blood to reach the penis. This can make erections more difficult.

Trouble With NO
Your body uses a chemical called nitric oxide (NO) to help you get an erection. NO tells the blood vessels in the penis to relax and open up, letting blood flow in. This is what causes an erection. When you’re dehydrated, your blood vessels are under stress and may not make enough NO. Also, dehydration can increase something called oxidative stress, which breaks down NO. That means even if your body tries to make NO, it might not work as well. Without enough NO, the blood vessels don’t open up properly, and that makes getting an erection more difficult. So, staying hydrated keeps your blood pressure steady and helps your body make the chemicals needed for healthy erections.
Taken together, these direct effects show that dehydration can create a “perfect storm” of physiological hurdles for an erection: less blood to fill the penis, narrower arteries, insufficient blood pressure, and a suboptimal chemical environment for vascular relaxation and hormonal support. It’s important to note that these changes mainly cause temporary erectile difficulties – for example, a man who is very dehydrated after intense exercise might notice a weaker erection until he rehydrates. Chronic dehydration (consistently not drinking enough fluids) could, over time, contribute to more persistent ED by continually straining the vascular system and hormonal balance.
How Dehydration Indirectly Affects Energy and Sexual Performance?
Dehydration doesn’t just affect your body physically; it also changes how you feel. When you don’t drink enough water, you might feel tired, cranky, or just off. These feelings can make it harder to enjoy or want intimacy. Here’s how being low on water can lead to problems like erectile dysfunction (ED):
Feeling Tired and Having Low Energy
Even a small amount of water loss in your body can make you feel weak and tired. That’s because your cells and organs don’t work as well, your blood doesn’t flow as smoothly, and your heart has to work harder to keep things moving. All of this can wear you out. If you try to be active, including during sex, you might run out of energy faster, get muscle cramps, or just not feel strong enough to keep going.
When your body is that tired, it’s harder to feel excited or stay in the mood. Erections might be weaker or harder to keep because your body isn’t focused on pleasure; it’s just trying to keep up. Think of it like a car running on an almost-empty tank. It won’t perform well until you refill it.
That’s why staying hydrated helps. When your body has enough water, your energy stays up, your muscles work better, and you’re more likely to feel good during physical activity. Drinking enough water can make a real difference in how you feel and how your body performs, including during intimate moments.
Mood, Stress, and Nerve Signals
Not drinking enough water doesn’t just affect your body; it also affects how your brain works and how you feel. Even mild dehydration can make you feel more tense, anxious, or forgetful. One study by Cambridge found that men who were just a little dehydrated felt more stressed and had a harder time remembering things.
This matters for sexual health because how you feel mentally plays a big part in getting and keeping an erection. Feeling stressed, irritated, or anxious from being dehydrated can stop the brain from sending the right signals to the body. Erections actually start in the brain, with feelings of attraction and relaxation. If you’re not feeling calm, the process may not work well.
When you’re dehydrated, your body also releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These activate your “fight or flight” system, which is the opposite of what you need to relax and feel aroused. This response can make erections more difficult.
Low Sex Drive and Dehydration
Not drinking enough water can do more than just make you tired or cranky; it can also lower your interest in sex. When you’re thirsty and uncomfortable, your body is in a kind of stress mode. And in that state, things like sex drive are not a priority. Over time, if you stay dehydrated, your body might even make less testosterone, the hormone that helps with sexual desire and erections. Even short-term dehydration can make you feel less in the mood simply because you’re not feeling your best.
Some people may notice they don’t feel interested in sex when they haven’t had enough to drink, like a “dry spell” both physically and emotionally. The good news is that this usually goes away once you start drinking enough water again. Getting rehydrated can help bring back your energy and mood, and that can improve your sex drive too.
Conclusion
You might not think water has anything to do with erections, but it actually does. When you’re dehydrated, your body doesn’t work as well. You have less blood flowing, your blood vessels tighten up, your hormones get out of balance, and you feel more tired; all of which can make it harder to get or keep an erection. The good news is that this kind of problem is easy to fix: just drink more water! Staying hydrated helps your blood move better, keeps your body and mood in balance, and can help improve sexual performance.
Most adult men should aim to drink about 6 to 8 glasses of water a day. If you’re exercising or it’s really hot outside, you might need more. Watch out for signs you’re not drinking enough, like dark yellow pee, dry mouth, dizziness, or feeling really tired. Catching these signs early can help you avoid bigger problems later, including problems in the bedroom. Drinking water should be part of your overall health routine, just like eating healthy, working out, cutting back on alcohol, and managing stress.
If you’re drinking enough water but still having trouble with erections, it’s a good idea to talk to a doctor. There could be other health issues going on. Dehydration might just be one part of the problem, but it’s still an important one. Something as simple as drinking water can make a big difference in how your body works, including your sexual health. So, keep a water bottle handy and stay hydrated, your body (and your partner) will be glad you did.
CONTACT US
If you have any question, please contact us at
Near Maxus Mall, Mira-Bhayander.
Thane-Mumbai – 401101
At FableWings, we work hard to make sure the health and wellness products we sell online follow all the rules and laws. Every product on fablewings.com comes from trusted companies that are allowed to make medicine and have trained experts checking the quality. Our goal is to give you safe, helpful products you can trust. Read more in our Disclaimer.

